Introduction
Today, businesses don’t operate on intuitions and correlated datasets. Organizations are heavily dependent on business intelligence (BI) to learn about their operations, predict performance, and make informed decisions. BI insights are as useful as the data, processes, and systems they work on. This gives rise to the concept of combining quality assurance (QA) with BI, which provides valuable insights, promotes smart decision-making, and supports strong governance.
As per this approach, accurate data has all the power; however, information itself cannot decide whether a business will prosper or not. With BI being a complex factor, the need for the implementation of effective and structured QA processes grows exponentially.
This blog provides an understanding of QA and BI while exploring the factors involved in these approaches. It also focuses on why the traditional QA approach fails and why the BI-based QA approach is crucial.
What is quality assurance?
QA is an efficient process that is adopted to make sure that the company’s products and services meet the pre-established standards and quality. This process helps prevent defects, maintain consistency, and enhance overall operations.
According to Dimension Market Research’s article ‘QA Services Market’, this industry is valued at $4.7 billion in 2025 and will reach $15.5 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 14.2% (i).
What is business intelligence?
BI is a strategy used by the organizations for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing datasets to make informed decisions. BI is responsible for converting raw data into valuable insights that provide a detailed overview of the organization’s performance, help identify market trends, and promote predicting future outcomes.
As per Precedence Research’s ‘Business Intelligence Market Expands with Embedded BI in Enterprise Applications’ article, the market value of the global BI industry is about $31.34 billion in 2025 and will grow with a CAGR of 7.26% to reach $63.17 billion by 2034 (ii).
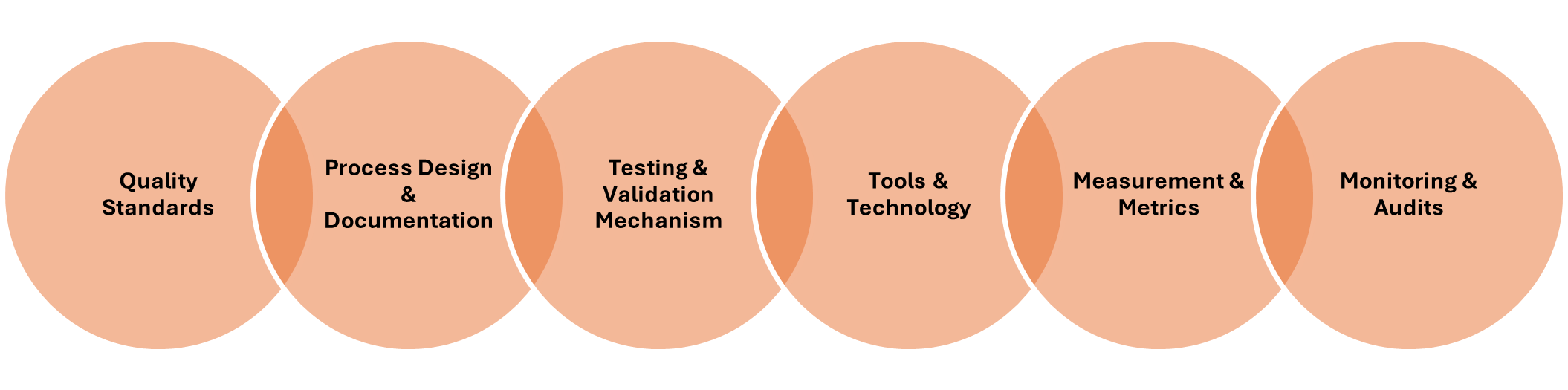
Factors Involved in QA
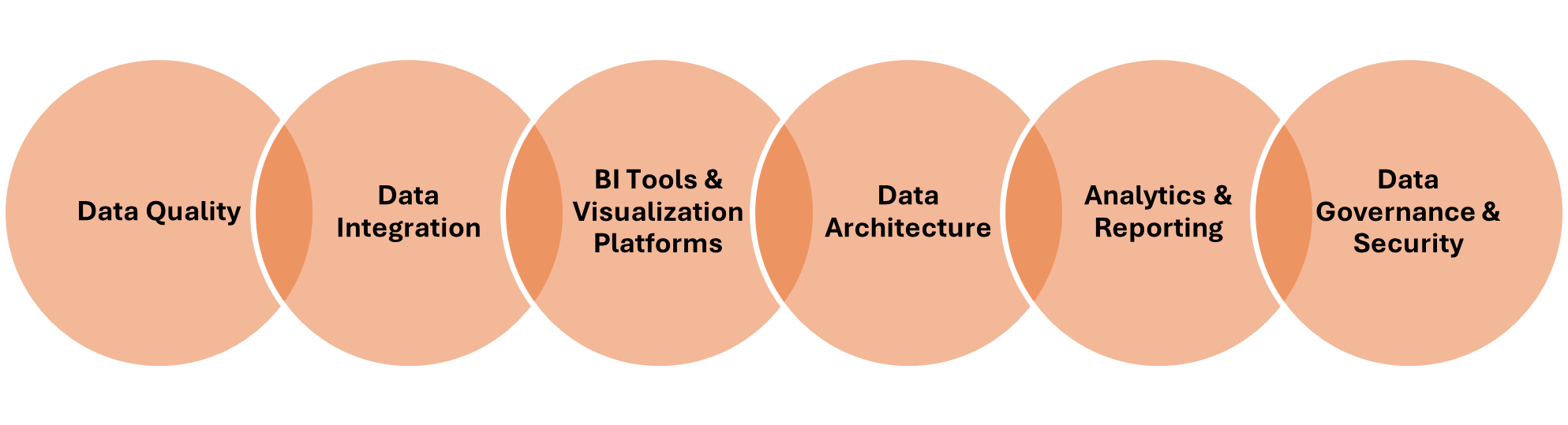
Factors Involved in BI
Why Traditional Call Center QA Falls Short?
Traditionally, the call center QA process includes auditing calls manually, scoring spreadsheets, and a waiting period for analysts’ judgment. Though organizations have been using this method for decades, it is no longer feasible in today’s scenario where the volume is high and there are multiple channel interactions. There are various limitations to the traditional QA approach, which are:
- Limited sample size (1% to 2% of total interactions);
- Time-consuming operations;
- Inconsistent scoring;
- Limited integration with existing business operations;
- Lack of proactive approach;
- Low Scalability.
“According to WNS’s ‘Global Analytics Survey’, about 60% of the businesses are planning to adopt AI technologies, including BI platforms (iii).”
What is BI testing strategy?
BI testing strategy is a controlled method that validates the organizational data, processes, and reporting in a BI ecosystem. This approach ensures high accuracy, consistency, performance, reliability, and overall security. In this modern testing, BI keeps its focus on data improvement, accurate reporting, transformation, and system performance across large datasets.
In other words, the BI testing strategy ensures that the data lifecycle is checked thoroughly, i.e., from ingestion to presentation.
“As per PractiTest’s State of Testing Report 2025, only 1% of the businesses have fully automated testing efforts and eliminated manual testing (iv).”
Core Components of a BI Testing Strategy
As a BI testing strategy is crucial for a successful call center, there are various components that make it effective. The pillars of BI testing strategy include:
- Define Test Scope: This step outlines the scope of BI testing. This includes data source systems, data models, data layers, security, dashboards, and performance. Defining the BI testing scope helps prevent shortfalls and promotes correlation amongst QA teams, BI analysts, developers, and business stakeholders.
- Establish KPIs and analysis requirements: Predefined and precise business requirements and definitions are essential for BI testing. Without pre-established terms and requirements, BI testing can lead to inconsistency and ambiguity.
- Test Planning: This component provides a detailed overview of how BI testing will be done. It includes predefining roles and responsibilities, data preparation requirements, tools and automation, and test entry-exit standards. This reduces unexpected delays and supports test coverage.
- Test Cases & Scenarios: It is a foundational step that includes intricate data flows, data transformation, and reporting systems. BI test cases are established to promote data accuracy, data quality, performance, and usability.
- Test Data Preparation: BI testing is based on realistic, accurate, and multiple sources of datasets. The data quality directly influences the reliability and dependency on the testing outcomes.
- Execute Different Types of BI Testing: There are various BI tests, which include ETL/ELT testing, data model testing, report & dashboard testing, security testing, performance & load testing, and regression & continuous testing.
- Identify Defects: It is essential that once a defect is discovered, it must be logged in, dealt with on priority, and retested. This ensures that an effective defect lifecycle is maintained and timely resolution is provided.
- Validate User Acceptance Testing (UAT): As soon as QA testing is completed, conduct UAT for business participants. Once it is signed, allow the QA team to perform product validation to ensure dashboard stability and data correctness.
“As per Sigma’s ‘The 2025 State of BI Report’, 83% of the businesses are unable to access data in real time (v).”
BI Testing Strategy Roadmap
To implement a BI-based QA strategy, it is essential to understand every step. Here are the steps that are required to be followed for implementing this strategy effectively:
Step 1. Foundation & Planning: This step lays down the pathway to implement BI-based QA. It includes defining BI objectives and goals, data governance framework, data sources, and tools to be used.
Step 2. Test Design: After establishing the foundation, it is essential to test the process design. This includes mapping data lineage, defining test scenarios, designing test data, and setting up metrics and KPIs.
Step 3. Build & Execute Testing: Once test design is completed, start testing the ETL/ELT pipeline, validate data test models, test data transformation, record defects, and keep track of dispute resolutions. This step also includes testing the user interface for dashboards and executing performance-based tests under the expected workload.
Step 4. UAT & Deployment: This step ensures validating end users, aligning with business requirements, and being ready for production deployment. It focuses on business validation, user acceptance, and real-world willingness.
Step 5. Continuous Enhancement: As the business world changes continuously, the BI atmosphere also changes constantly. Continuous improvement includes updating new sources, new KPIs, business guidelines, and data transformations as per business needs.
As per PractiTest’s State of Testing Report 2025, about 41% of the businesses are using AI tools for test case creation, 20% for test planning, 18% for test data management, and 19% for test reporting and insights (iv).”
How Is BI-Based QA Different?
The BI-based QA method brings together the best of two worlds, i.e., it combines traditional quality monitoring with advanced data analytics, automation, and reporting intelligence. It modernizes QA by utilizing the overall data and not just call data, which are being listened to by evaluators. This is how a BI-based QA strategy modifies the company’s operations:
- 100% data auditing and avoiding sampling calls;
- Automated data recordings;
- Proactive quality management;
- Transparent and detailed overview on advanced dashboards;
- Generating real-time insights;
- Data-based evaluation;
- Multi-channel auditing.
How Do QA and BI Work Together?
Let’s take a dive and explore how this combination works.
1. Data-based Test Planning: By implementing BI tools, businesses can generate valuable insights, customer pain points, and past issues density. QA teams can use such information to test highly used features, strengthen automation, predict potential issues, and prepare to provide quality experiences.
2. Predictive Quality Analysis: The integration of advanced BI skills with QA data, businesses can forecast:
- Potential issues to occur;
- High-risk areas;
- Limitation of present test coverage;
- Whether the current system can handle peak hour risk.
These advanced analytics can provide a head start to the QA team to prevent potential issues and opt for a proactive approach.
- Informed Decision Making: We’ve seen supervisors struggle with deciding whether their products and services are good enough or not. QA metrics along with BI dashboards provide a clear picture by showing performance patterns, issues severity, test execution changes, and unresolved issue affecting business outcomes. BI with a QA approach leads to decision-making based on evidence and not intuitions.
- Root-cause Analysis with BI Tools: When an issue arises, QA teams with BI tools can assess the system logs, customer activity information, and past patterns to highlight the root causes immediately. This promotes quick resolutions, improves operations, and enhances accuracy.
The Future of the BI-based QA Approach
Digital transformation has changed the business world, and it promotes growth and success of the businesses. We’ve listed the best future trends that support intertwined QA and BI.
- AI-based Test Optimization: AI automatically assesses QA datasets to generate test scenarios, forecast gaps, and streamline test planning based on customer transactional behavior.
- Real-time Quality Intelligence: BI dashboards display the operational performance, metrics, and error logs, ultimately streamlining the quality operations.
- BI Insight Testing: BI creates 360-degree preview of pre-development strategies and post-release experience.
NEQQO is one such advanced platform that brings together quality management, advanced reporting, and business insights to improve and streamline the business operations and performance.
Conclusion
The combination of QA and BI marks a fundamental transformation in how companies make informed decisions and sustain operational excellence. QA establishes the foundation of quality, user-friendly experience, and reliable products, whereas BI enhances the operations by generating valuable insights, reshaping operational strategies, and making informed decisions.
Together, QA and BI create a crucial partnership that minimizes risk, promotes creative innovation, and improves customer satisfaction. It is essential that businesses embrace this combination to explore the complex markets, adapt instantly to transform, and provide valuable outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the key factors of quality assurance?
There are various factors involved in the implementation of quality assurance:
- Quality standards
- Performance metrics or KPIs
- Defect prevention
- Testing phase
- Process documentation
2. Why does traditional QA fail in today’s call center industry?
Traditional QA relies on manual call monitoring, limited sampling, lack of integration, and slow processes. This approach struggles to manage multi-channel interactions and high call volumes in modern call center environments.
3. What are the benefits of implementing a BI-based QA strategy?
A BI-based QA approach improves overall operational visibility, enhances accuracy, enables real-time insights, supports multi-channel evaluations, and aligns QA processes with business outcomes.
4. How does BI enhance the productivity of companies?
BI consolidates data from multiple sources, generates detailed reports, and presents operational performance through dashboards. This reduces the time spent collecting data and helps teams analyse issues quickly to deliver effective solutions.
Sources
(i). QA Services Market
(ii). Business Intelligence Market Expands with Embedded BI in Enterprise Applications
(iii). Global Analytics Survey



